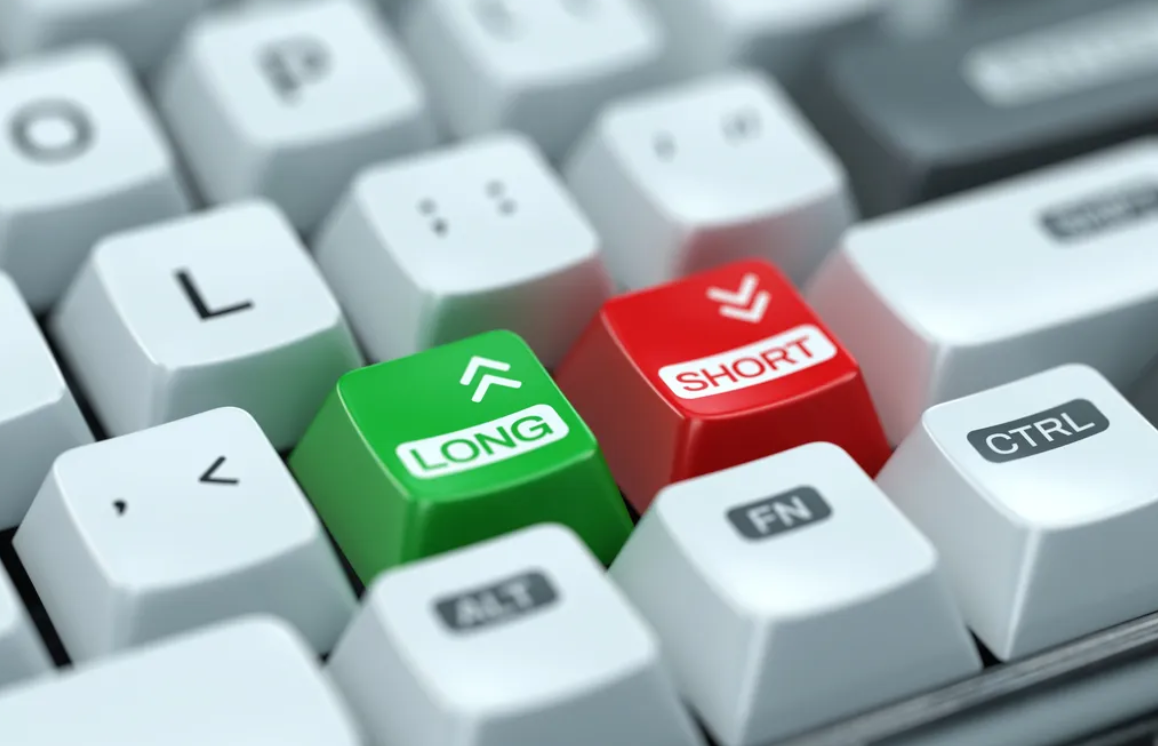
In the world of finance, the term “shorting a stock” often evokes curiosity and fascination. It’s a financial maneuver that’s often depicted in movies as a surefire way to make a fortune, or to bring about the downfall of a shady corporation. But what exactly is shorting a stock? In this article, we’ll delve into the intricacies of short selling, demystify its mechanics, discuss its potential risks and rewards, and explore its ethical dimensions.
Short Selling Explained
At its core, shorting a stock is a bearish investment strategy. When investors short a stock, they’re essentially betting that the stock’s price will fall. Here’s how it works:
Borrowing Shares: The first step in shorting a stock involves borrowing shares from a broker or another investor. This borrowed stock is sold immediately on the open market.
Selling High, Buying Low: The goal of the short seller is to sell the borrowed shares at a higher price and then buy them back later at a lower price. This is the opposite of the typical buy-low, sell-high strategy.
Returning Borrowed Shares: Once the shares are bought back, they are returned to the lender, and the short position is closed.
Shorting vs. Traditional Investing
Short selling stands in stark contrast to the more conventional strategy of buying shares with the expectation that their value will increase over time. While traditional investing is about long-term gains and holding onto assets, short selling is all about capitalizing on falling prices and profiting from market downturns.
Risk and Reward
The potential rewards of short selling are tantalizing, but the risks are equally daunting.
Rewards:
Profits in a Bear Market: Shorting allows investors to make money even when the broader market is in decline.
Diversification: Short selling can act as a hedge against losses in long positions, providing diversification in one’s portfolio.
Risks:
Unlimited Losses: Unlike traditional investing, where losses are capped at the initial investment, short sellers can face unlimited losses if the stock’s price rises substantially.
Margin Calls: If a short position moves against the investor, they may receive a margin call, requiring additional capital to maintain the position.
The Ethical Debate
Short selling has long been a subject of ethical debate. Critics argue that it can be used to manipulate markets, spread false information, and drive down the prices of companies unfairly. Proponents, on the other hand, argue that short sellers play a vital role in uncovering corporate misconduct and ensuring transparency.
Regulations and Restrictions
To mitigate some of the risks associated with short selling, many financial markets have established regulations and restrictions. For instance, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has implemented the “uptick rule” to prevent short sellers from driving down a stock’s price too aggressively. In addition, some countries have outright bans on short selling during times of extreme market volatility to prevent further market turmoil.
The Psychology of Short Selling
Short selling also delves into the realm of human psychology. It requires a unique mindset characterized by skepticism, analytical thinking, and the ability to go against the crowd. Short sellers often conduct in-depth research to identify overvalued or fraudulent companies, which can lead to a heightened sense of vigilance.
Short Squeezes and GameStop
One of the most iconic short squeezes in recent memory involved GameStop, a video game retailer. A group of retail investors, organized through social media platforms like Reddit, noticed that hedge funds had heavily shorted GameStop stock. They banded together to drive up the stock’s price, causing massive losses for the short sellers and a historic short squeeze.
The GameStop saga highlights the power of collective action in today’s interconnected financial world, where a determined group of individuals can take on Wall Street titans.
Shorting a stock is a complex and controversial financial strategy that exists at the intersection of risk, reward, and ethics. While it can be a profitable way to navigate bear markets and uncover corporate misconduct, it also carries the potential for significant losses and market manipulation. Understanding the mechanics and implications of short selling is essential for any investor looking to explore this unique facet of the financial world. As with all investment strategies, thorough research and a clear understanding of one’s risk tolerance are paramount in making informed decisions in the world of finance.